2 SnpEff
2.1 Introduction
SnpEff annotates genetic variants and predicts the functional effects. The output includes a VCF file with annotations that indicate what kind of mutation it is (e.g. introduction of a stop codon) and the predicted effect (low, moderate, high, modifier). In this study, we focus on high impact mutations, which include loss of function (LoF) and nonsense mediate decay (NMD) mutations.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Building the database
As the black grouse (Lyrurus tetrix) is no common model species with a pre-built database, a custom database was built from the annotation files in .gff format provided by Cantata Bio.
To build a custom database, five files are required: the gff file containing the gene annotation, the reference genome, and then three files containing information about the coding regions (cds.fa; a fasta file containing the coding regions only), the genes (genes.fa; a fasta file containing the genes only) and a file with the protein sequences (proteins.fa; a fasta file with the protein sequences). Two softwares were used to construct these three fasta files: gff3_to_fasta and AGAT.
gff3_to_fasta -g data/genomic/refgenome/PO2979_Lyrurus_tetrix_black_grouse.annotation.gff \
-f data/genomic/refgenome/PO2979_Lyrurus_tetrix_black_grouse.RepeatMasked.fasta -st cds -d complete -o data/genomic/refgenome/lyrurus_tetrix/cds.fa
gff3_to_fasta -g data/genomic/refgenome/PO2979_Lyrurus_tetrix_black_grouse.annotation.gff \
-f data/genomic/refgenome/PO2979_Lyrurus_tetrix_black_grouse.RepeatMasked.fasta -st gene -d complete -o data/genomic/refgenome/lyrurus_tetrix/genes.fa Similarly, the protein sequences were constructed with AGAT
agat_sp_extract_sequences.pl --gff data/genomic/refgenome/PO2979_Lyrurus_tetrix_black_grouse.annotation.gff -f \
data/genomic/refgenome/PO2979_Lyrurus_tetrix_black_grouse.RepeatMasked.fasta -p -o \
data/genomic/refgenome/lyrurus_tetrix/protein.faThen, the database was built (and automatically checked).
java -jar snpEff.jar build -gff3 -v data/genomic/refgenome/lyrurus_tetrixOnce the database is ready, we can run SnpEff to create the annotated vcf file.
java -Xmx8g -jar snpEff.jar ann -stats \
-no-downstream -no-intergenic -no-intron -no-upstream -no-utr -v \
lyrurus_tetrix data/genomic/intermediate/ltet_snps_filtered.vcf > data/genomic/intermediate/snpef/ltet_ann_snp_output.vcf2.2.2 Ancestral alleles
SnpEff annotates mutations according to the change from the reference allele to the focal allele. Hence, it assumes that the reference allele is the ‘better’ one and that a mutation that changes the transcription of this reference allele is detrimental. To allow this assumption to be better met, we used the ancestral genome as a reference, instead of the reference genome itself (i.e. we polarized the genome). This ancestral genome is constructed by cactus, and represents the most recent common ancestor between black grouse (L. tetrix) and Lagoplus leucura (white tailed ptarmigan). This way, any derived allele was assumed to be ‘deleterious’ compared to the ancestral allele, as opposed to a reference-non reference comparison.
2.2.3 Filtering
We then used SnpSift to filter annotated mutations based on the four impact categories: modifier, low, moderate and high impact using the following commands.
## High impact
zcat output/ancestral/ltet_filtered_ann_aa.vcf.gz | java -jar src/SnpSift.jar filter " ( ANN[*].IMPACT = 'HIGH' )" > data/genomic/intermediate/snpef/ltet_ann_aa_snp_output_HIGH.vcf
gzip data/genomic/intermediate/snpef/ltet_ann_aa_snp_output_HIGH.vcf
## Moderate
zcat output/ancestral/ltet_filtered_ann_aa.vcf.gz | java -jar src/SnpSift.jar filter " ( ANN[*].IMPACT = 'MODERATE')" > data/genomic/intermediate/snpef/ltet_ann_aa_snp_output_moderate.vcf
gzip data/genomic/intermediate/snpef/ltet_ann_aa_snp_output_moderate.vcf
## Low
zcat output/ancestral/ltet_filtered_ann_aa.vcf.gz | java -jar src/SnpSift.jar filter " ( ANN[*].IMPACT = 'LOW') " > data/genomic/intermediate/snpef/ltet_ann_aa_snp_output_low.vcf
gzip data/genomic/intermediate/snpef/ltet_ann_aa_snp_output_low.vcf
2.3 Results
We identified 5,341 high impact mutations:
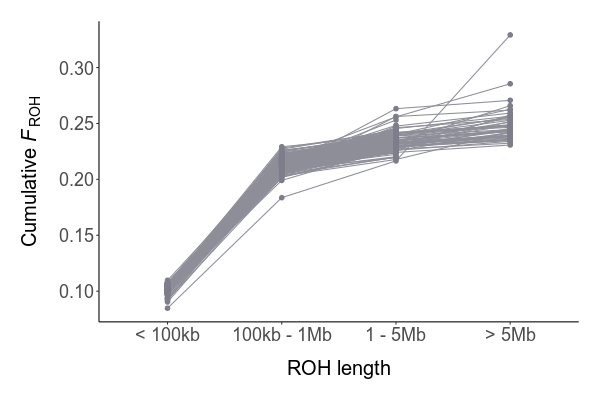
Existing of mostly LoF mutations and gained stop codons (non-mutually exclusive)
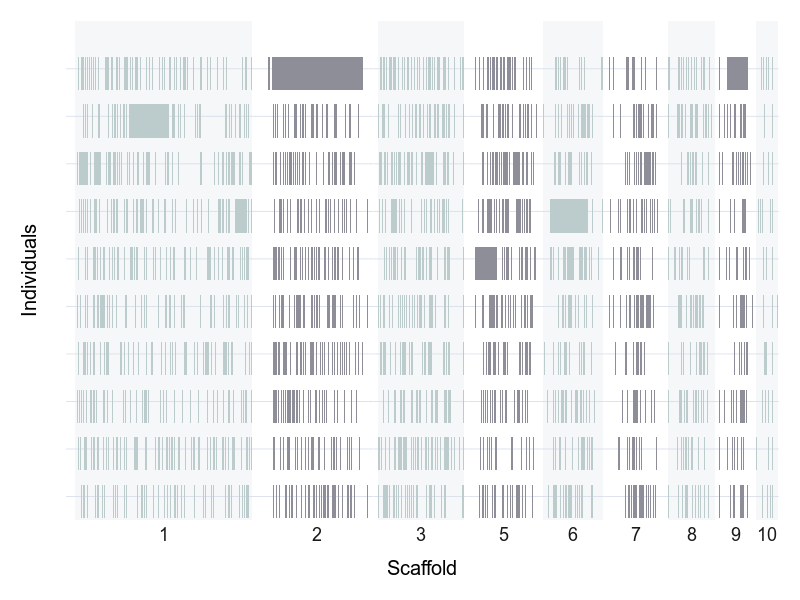
The mutations in the ‘high impact’ category were used to calculate individual genomic mutation load estimates.